| TRI-p-CRESYL PHOSPHATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO | 78-32-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 201-105-6 | |
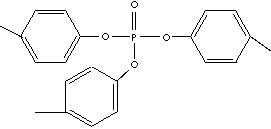
| FORMULA | (CH3C6H40)3PO | |
| MOL WT. | 368.37 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Tris(p-cresyl) phosphate; | |
| Triparacresyl phospate; p-Cresyl phosphate; p-Tolyl phosphate; Tris(p-cresyl) phosphate; Tris(p-methylphenyl) phosphate; Tris(p-tolyl) phosphate; Phosphoric acid, Tri-p-tolyl ester; m-Trioyl Phosphate; Phosphoric acid, tris(4-methylphenyl) ester; Phosphoric acid tris(4-methylphenyl) ester; p-Trikresylphosphate (German); Tri-4-Methylphenyl Phosphate; | ||
| SMILES | cresols, phosphorus oxychloride | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Pale yellow semi-solid |
|
| MELTING POINT | 76 - 78 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
|
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble |
|
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
|
|
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| HENRY'S LAW |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
| Tricresyl Phosphate is used as a plasticizer for PVC, rubber and plastics. It is used as an ingredient for flame-retardant in plastics, rubbers and in hydraulic systems. It is used as a heat exchange media. It is used a solvent and thinner for nitrocellulose, paints and varnishes. It is also used as an additive in high-pressure cooling lubricants. It is used as a lead scavenger in gasoline. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
|
|
|
ACID NUMBER |
|
|
| DENSITY |
|
|
| COLOR, HAZEN | ||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
|
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN N, Risk Phrases: 21/22-51/53, Safety Phrases: 28A-37-45-61 | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CRESOL |
||
Cresols are methyl substituted phenols at relative to the hydroxyl group,
ortho-,
meta-, and para-cresol. There are three structural isomers. The names of the
three compounds indicate which of the hydrogens on the benzene ring portion of
the molecule have been replaced. They are obtained from coal tar or petroleum
as by-products in the fractional distillation and in coal
gasification. They are also formed as by-products during
the combustion of wood. The various isomers can
be manufactured by the methylation of phenol, toluene sulfonation
and alkaline hydrolysis, or the hydrolysis of 2-isopropyltoluene
or alkaline chlorotoluene.
Because the boiling points of these three compounds are nearly the same, a
separation of a mixture of the three into its pure components is impractical.
They are highly flammable and soluble in water, ethanol, ether, acetone and
alkali hydroxides. The mixture of cresols obtained from coal tar is called
cresylic acid, an important technical product used as a disinfectant and in the
manufacture of resins and tricresyl phosphate. Cresylic acid also refs to the
mixture of phenols containing varying amounts of xylenols, cresols, and other
high-boiling fractions, but not more than 5 percent phenol. Commercial cresols
are prepared in a wide range of grades and purities to meet the user's
requirements. It is a liquid from clear to brown and is toxic to animals
including human. It is corrosive and is a more powerful disinfectant and
antiseptic than phenol. The primary use is for sterilizing as disinfectants and
deodorizers, and pesticides. Its solution is used as household cleaners as a
disinfectant. Creosote products are
mixtures of many aromatic hydrocarbons including phenols and cresols. Creosote
obtained from coal tar is poisonous and provides protection against fungi,
shipworms, termites, and psoriasis. It is used chiefly as a wood preservative,
e.g., in wooden poles, railroad ties, and timber. They are also used as animal
and bird repellents. Animals may suffer skin irritation or ulceration from
creosote treated wood. Coal tar creosote and its derivatives are the most widely
used wood preservatives. Wood tar creosote is a mixture of chiefly guaiacol,
creosols and other phenolic compounds obtained from wood tar (mainly beech) by
distillation between 203 and 220 C. It is insoluble in water, soluble in
methanol, acetone. It is used as an external antiseptic, expectorant, gastric
sedative, deodorant, and as an antiseptic parasiticide veterinary use in the
form of creosote carbonate. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and
vanillin. Each cresols are used as
solvents or disinfectants and as useful as raw materials for various chemical
products including;
Cresols undergo electrophilic substitution reactions such as chlorination, bromination, sulfonation and nitration at the vacant position. They also undergo condensation reactions with aldehydes, ketones or dienes. O-cresol is a starting material for the synthesis of herbicides such as 4,6-dinitro-o-cresol (DNOC) and 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (MCPA). Meta-cresol is used in the manufacture of explosives. Meta and para-cresol are used in phenol-formaldehyde resins and are converted to tricresyl phosphate used as a plasticizer and gasoline additive and antioxidants such as di-tert-butylcresols (BHT). Ortho- and para-cresols are used in the production of lubricating oils and motor fuels. |
||